How to File ITR Online for Salaried Employee 2024-25: ITR-1 form is available online for free e-Filing for Assessment Year 2024-2025 (AY 2024-25) on official website IncomeTaxindiaeFiling.gov.in. Now, you can submit ITR Form and pay income tax securely from any place by using internet-banking facility of the authorised banks.
Income Tax Return (ITR) online filing becomes very simple and easy after the introduction of e-payment facility. Online filing of ITR-1 and payment of online income tax is time saving, simple and safe.
Did you know? More than 101.61 million Individual person registered for e-Filing their return of Income online. Facility is also available for e-Verify your ITR-1 using Aadhaar OTP, Net Banking, Pre-Validated Bank Account and Pre-Validated Demat Account.
Submit your income tax return before 31-July-2024 for taxable income earned during April 2023 to March 2024 i.e. previous year 2023-24. In this article, we will learn all about ITR-1 SAHAJ form e-Filing for AY 2024-25 in relation to PY 2023-24.
What is ITR-1 SAHAJ Form?
ITR-1 form is a type of income tax return for Individual taxpayers. ITR full form is Income Tax Return and it also known as SAHAJ form. It is widely used by Individuals to file their Tax Returns with the Income Tax Department of India.
ITR 1 is mainly used by salaried employees and retired persons to pay tax on their salary or pension income. The due date of filing the ITR-1 form for the Financial Year 2023-24 is July 31, 2024.
A “Taxpayer” is a person who either has filed a return of income for the relevant Assessment Year or in whose case tax has been deducted at source (TDS) in the relevant Financial Year but the taxpayer has not filed the return of income. That means taxpayer means a person who filed ITR or TDS deducted but he has not filed ITR.
Is it Compulsory to file Income Tax Return?
Every individual has to file the return of income if his total income, without giving effect to deduction under section 80C to 80U, exceeds the exemption limit.
If you fails to file the return of income within the time limit i.e. 31-Aug-2023, then as per section 139(4) you can file a belated return. A belated return can be filed at any time before the end of the relevant assessment year i.e. 31-March-2024.
However, if assessee failed to furnish income tax return within due date as prescribed in section 139(1) then he is required to pay:-
- ₹5000 if ITR filed on or before 31 December of assessment year.
- ₹10,000 in any other case.
However, if total income of the person does not exceeds ₹5 lakh then fee payable shall be ₹1000.
Who is Eligible to File New ITR 1 for AY 2024-25?
If you satisfy the following criteria, you are eligible to file your Income Tax Return in Form [SAHAJ] (ITR-1) for assessment year 2024-25:
- Indian Resident: An individual who is a resident in India can file ITR-1. However, a person not ordinarily resident is not eligible to file ITR-1;
- Taxable Income: ITR-1 form is filed for total income is upto ₹50 Lakhs.
- Agricultural Income: If you have agricultural income upto ₹5000, you can file ITR-1 form.
- Salary Income: Income chargeable under the head ‘Salaries’ shall be submitted through ITR-1 Sahaj form. Salaried taxpayers file ITR1 for AY 2024-25.
- House Property: Income from one House Property;
- Interest income: ITR-1 used to file income from other sources i.e. Interest income etc.
In other words, New ITR-1 Form is applicable for individual taxpayer having total income up to ₹50 lakh from salaries, one House Property, Other Sources (Interest etc.), and Agricultural Income upto ₹5 thousand.
Who cannot file New ITR 1 for AY 2024-25?
ITR-1 form is not applicable for a person who has/is:-
- Assets (including financial interest in any entity) located outside India;
- Signing authority in any account located outside India;
- Income from any source outside India;
- Income to be apportioned in accordance with provisions of section 5A;
- Claimed deduction under section 57, other than deduction claimed u/s 57(iia);
- A director in any company;
- held any unlisted equity share at any time during the previous year;
- Assessable for the whole or any part of the income on which tax has been deducted at source in the hands of a person other than the assesse;
- Claimed any relief of tax under section 90 or 90A or deduction of tax under section 91;
- Agricultural income, exceeding five thousand rupees;
- Total income, exceeding fifty lakh rupees;
- Income taxable under section 115BBDA; or
- Income of the nature referred to in section 115BBE;
Structure of ITR-1 SAHAJ Form for Financial Year 2023-2024
ITR-1 Form e-Filing AY 2024-25 for Salary and Interest Income. Income tax return form ITR-1 is divided into 5 parts and Schedules for assessment year 2024-25 in relation to previous year 2023-24.
ITR-1 PART A General Information
Under Part-A of ITR-1 you have to provide the following personal information:
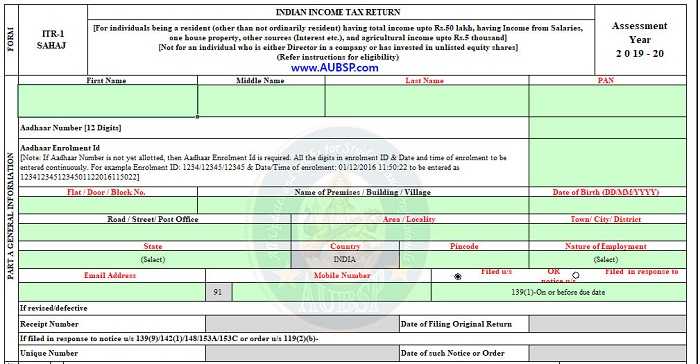
Assessee Name:
Name of assessee or taxpayer person. You have to enter your first name, middle name and last name in tax return. Providing your title, i.e. Last Name is compulsory in ITR 1.
Taxpayer PAN:
Enter your valid 10 characters PAN card number. It is mandatory to provide your Permanent Account Number (PAN) as provided by the income tax department.
If you do not have PAN card, you may submit an online application from the official website of UTIITSL or NSDL.
Aadhaar Number:
You are required to enter your 12 digit Aadhaar card number. If you have no Aadhaar card, you may skip this field. However, if you have applied for Aadhaar card, please provide your Aadhaar Enrolment Id.
The top of your acknowledgement slip contains 14 digit enrolment number (1234/54321/12345) and the 14 digit date and time (dd/mm/yyyy hh:mm:ss) of enrolment. These 28 digits together form your Aadhaar Enrolment ID.
Address of Assessee:
You have to enter your complete address in ITR-1 form. These are the following fields for providing address of assessee:
- Flat/ Door/ Block No.
- Name of Premises/ Building/ Village (Optional)
- Road/ Street/ Post Office (Optional)
- Area/ Locality
- Town/ City/ District
- State
- Country
- Pin Code
DOB of Taxpayer:
Bate of Birth (DOB) of assessee is compulsory in DD/MM/YYYY format.
Email Address:
Enter your valid email address, which will be used to communicate you regarding your income tax return.
Mobile Number:
Provide your 10 digit active mobile number. You will receive OTP and other relevant information regarding your return of income.
Nature of Employment:
You have to select your nature of employment from options viz. Government employee, Public Sector Undertaking, Pensioner or Other.
ITR-1 filed within due date:
If you are filing your ITR-1 within due date i.e. 31st July, 2019, select option “Filed u/s 139(1) – on or before due date”. You may choose any one from options i.e. 139(4) – Belated, 139(5) – Revised, 119(2)(b) – after condonation of delay.
Taxpayer provide date of filing original return and receipt number for filing revised or defective return of Income.
ITR-1 filed in response to Notice/Order:
In case of filing return in response of notice from income tax department, please select appropriate option. For example- If filed in response to notice u/s:
- 139(9) – Defective Return.
- 142(1) – Inquiry before assessment.
- 148 – Issue of notice where income has escaped assessment.
- 153A – Assessment in case of search or requisition.
- 153C – Assessment of income of any other person.
- 119(2)(b) – Order to admit an application or claim for any exemption, deduction, refund or any other relief under Income-tax Act, 1961.
Assessee required to provide date of such notice or order and unique number if filing return in response to notice u/s 139(9)/ 142(1)/ 148/ 153A/ 153C or order u/s 119(2)(b) of Income-tax Act, 1961.
PART B Gross Total Income
Under PART-B, the taxpayer calculate Gross Total Income (GTI) for relevant assessment year. As we know, the ITR-1 filed for income earned from mainly three sources viz. Salary/Pension, House Property and Other sources.
How to file income tax return online for salaried employee 2024-25?
If you are not able to file your Income Tax Return, please sit back and let us file your ITR Form within due date.
1. Source of Income – Salary
In this part, you have to provide all details related to your salary income. You may use data of Form No. 16 for filing details required in ITR-1 form. You may ask your employer to provide Form No. 16, a certificate under section 203 of the Income-tax Act, 1961 for tax deducted at source on salary.
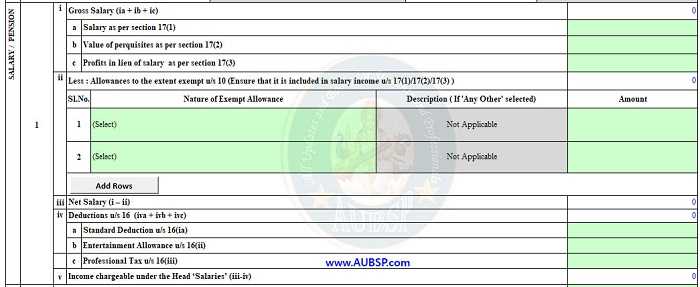
PART A of Form 16 contain summary of amount paid/credited and tax deducted at source thereon in respect of the employee. On the other hand, details of income chargeable under head Salary and deductions under Chapter VI-A (80C to 80U) are there in PART B (Annexure) of Form 16.
While filing your ITR-1 make sure to enter amount of the following particulars accurately:
- Salary as per section 17(1)
- Value of perquisites as per section 17(2)
- Profits in lieu of salary as per section 17(3)
Exempted Allowances: Allowances to the extent exempt under sections 10 of Income=tax Act, 1961:
- Leave Travel concession/assistance [Section 10(5)]
- Remuneration received as an official, by whatever name called, of an embassy, high commission etc. [Section 10(6)]
- Allowances or perquisites paid or allowed as such outside India by the Government to a citizen of India for rendering service outside India. [Sec 10(7)]
- Death-cum-retirement gratuity received. [Sec 10(10)]
- Commuted value of pension received. [Sec 10(10A)]
- Earned leave encashment on Retirement. [Sec 10(10AA)]
- Retrenchment Compensation received in respect of schemes not approved. [Sec 10(10B)(i)]
- Retrenchment Compensation received in respect of approved scheme. [Sec 10(10B)(ii)]
- Amount received/receivable on voluntary retirement or termination of service. [Sec 10(10C)]
- Tax paid by employer on non-monetary perquisite. [Sec 10(10CC)]
- Allowance to meet expenditure incurred on house rent. [Sec 10(13A)]
- Prescribed Allowances or benefits (not in a nature of perquisite) specifically granted to meet expenses wholly, necessarily and exclusively and to the extent actually incurred, in performance of duties of office or employment. [Sec 10(14)(i)]
- Prescribed Allowances or benefits granted to meet personal expenses in performance of duties of office or employment or to compensate him for increased cost of living. [Sec 10(14)(ii)]
Please ensure that the above exempted allowances are included in salary income u/s 17 of IT Act.
2. Source of Income – House Property
Assessee has to fill up all details for income from the single house property for relevant assessment year. Enter the amount of gross rent received or receivable or letable value during the year and tax paid to local authorities in respective field of ITR-1.

Note that maximum Loss from House property that can be set-off is ₹2 Lakh. To avail the benefit of carry forward and set-off of loss, please use ITR-2 Form.
3. Source of Income – Other Sources
In the ITR-1, five sources of ‘Other income’ are specified, namely interest from savings account, interest from deposits (Bank/Post office/Cooperative society), interest from income tax refund, family pension and any other.

If you select nature of income as “Any Other”, then you are required to provide the details of the income received.
Section 80TTA allows an individual or a Hindu undivided family to claim upto ₹10000 as a deduction from interest income received from savings accounts with banks and post offices.
Section 80TTB inserted for senior citizen by the Finance Act, 2018, w.e.f. 1-4-2019. That means, from financial year 2018-19, senior citizens can claim deduction up to ₹50000 for interest on deposits with bank, co-operative society and post office fixed deposits.
PART C – Deductions and Taxable Total Income
- 80C – Life insurance premia, deferred annuity, contributions to provident fund, subscription to certain equity shares or debentures, etc.
- 80CCC – Payment in respect Pension Fund
- 80CCD(1) – Contribution to pension scheme of Central Government
- 80CCD(1B) – Contribution to pension scheme of Central Government
- 80CCD(2) – Contribution to pension scheme of Central Government by employer
- 80CCG – Investment made under an equity savings scheme
- 80D deductions for
- Health insurance premium
- Medical expenditure
- Preventive health check-up
- 80DD – Maintenance including medical treatment of a dependent who is a person with disability
- 80DDB – Medical treatment of specified disease
- 80E – Interest on loan taken for higher education
- 80EE – Interest on loan taken for residential house property
- 80G – Donations to certain funds, charitable institutions, etc.
- 80GG – Rent paid
- 80GGA – Certain donations for scientific research or rural development
- 80GGC – Donation to Political party
- 80TTA – Interest on deposits in savings Accounts
- 80TTB– Interest on deposits in case of senior citizens
- 80U – In case of a person with disability
PART D – Computation of Tax Payable
Firstly, you have to provide detail of exempted income for reporting purpose:
- Agriculture Income (less than equal to Rs. 5000)
- Any amount from the Central/State Govt./local authority by way of compensation on account of any disaster [Sec 10(10BC)]
- Any sum received under a life insurance policy, including the sum allocated by way of bonus on such policy except sum as mentioned in sub-clause (a) to (d) of Sec.10(1) [Sec 10(10D)]
- Statutory Provident Fund received [Sec 10(11)]
- Recognized Provident Fund received [Sec 10(12)]
- Approved superannuation fund received [Sec 10(13)]
- Scholarships granted to meet the cost of education [Sec 10(16)]
- Allowance MP/MLA/MLC [Sec 10(17)]
- Award instituted by Government [Sec 10(17A)]
- Pension received by winner of “Param Vir Chakra” or “Maha Vir Chakra” or “Vir Chakra” or such other gallantry award [Sec 10(18)]
- Armed Forces Family pension in case of death during operational duty [Sec 10(19)]
- Any income as referred to in section 10(26) [Sec 10(26)]
- Any income as referred to in section 10(26AAA) [Sec 10(26AAA)]
- Exempted Dividend Income [Sec 10(34)]
Thereafter, you may claim rebate under section 87A and relief under section 89(1) of the Income-tax Act, 1961. Health and Education Cess would be @4% on tax payable after rebate.
Finally, interest u/s 234A, 234B, 234C and fee under section 234F shall be added to balance tax after relief u/s 89(1) of Income Tax Act, 1961.
PART E – Other Information
Details of all Bank Accounts held in India at any time during the previous year (excluding dormant accounts) shall be provided in schedule section.
Moreover, details of Advance Tax and Self-Assessment Tax payments shall be provided in ITR-1. You may enter details of TDS/TCS as per Form 16/16A/16C/27D issued by the Deductor(s)/ Employer(s)/ Payer(s)/ Collector(s) respectively.
